Calculating Overtime for Nonexempt Employees Working Two Jobs
When a nonexempt employee performs more than one job for the same employer, it can be challenging to determine the best way to pay for the hours worked in the second job and any resulting overtime.
One common scenario is when a nonexempt employee (e.g., a maintenance worker) also drives a bus, and due to the bus route hours the employee is not able to work eight hours a day in their primary job. While organizations handle pay determination in several different ways depending on the situation, some of the more common methods for this scenario include:
- Considering the position as a combined job where one rate of pay is paid for all work performed, and the rate is partway between the rates they would make in either job. This makes overtime calculations simpler because a blended rate is not required, but it can be expensive if the employer ends up paying a higher rate for the primary assignment than they otherwise would.
- Releasing someone from their regular job to do the secondary job, so there’s no need to double pay. In this scenario, the regular job is paid at 40 hours per week at the primary job’s rate of pay, even if the person is spending part of those 40 hours doing the secondary job. Work performed in the secondary job is only paid for time worked outside of the normal 40-hour work schedule. While this method does not make overtime calculations easier, it can be less expensive if the rate of pay is typically higher for the secondary job.
- Not annualizing pay and paying for time worked in each assignment as determined by timecard entries. This does not make overtime calculations any simpler because pay is not being handled through exceptions but rather through actual time recorded. While most employers choose to use blended rates for overtime calculations in this scenario, some choose the more complicated method where the employee agrees to be paid overtime based on which type of work they perform during any overtime hours.
Available Tools
To assist with blended rate calculations, TASB HR Services members can use the Blended Overtime Rate Calculation Worksheet found in the HR Library (member login required). For community colleges, see Blended Overtime Rate Calculation Worksheet - College. The tool allows the user to simply enter the rates and hours worked and let the worksheet complete the calculations for you. An example is shown below.
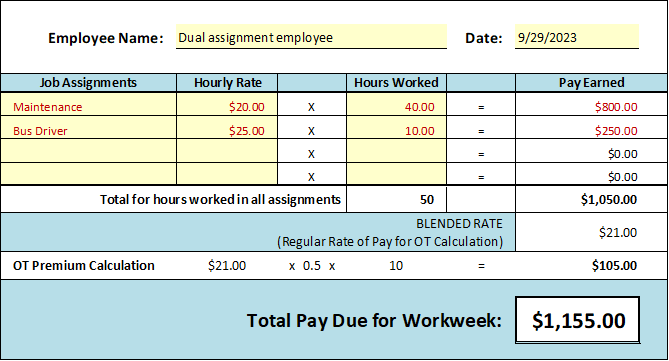
Additionally, a more thorough review of overtime with additional examples and calculation scenarios is available in The Administrator’s Guide to the Fair Labor Standards Act, available in the TASB Store.

Keith McLemore
Keith McLemore joined HR Services in 2015 and assists districts with compensation planning and development. He has 17 years of experience traveling the state supporting public education employees.
McLemore received a bachelor’s degree from Southwestern University and a master’s degree from Texas Tech University, both with a focus on research analysis and design. He is a SHRM-CP.
HR Services

Subscribe to HRX
Stay up to date with all the latest HR news and trends by joining the HRX mailing list!





